The 2N3904 and 2N3906 are both commonly used bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) belonging to the general-purpose NPN and PNP transistor families, respectively. While they are complementary pairs and share similar naming conventions, there are fundamental differences between the two. Let's understand these differences:
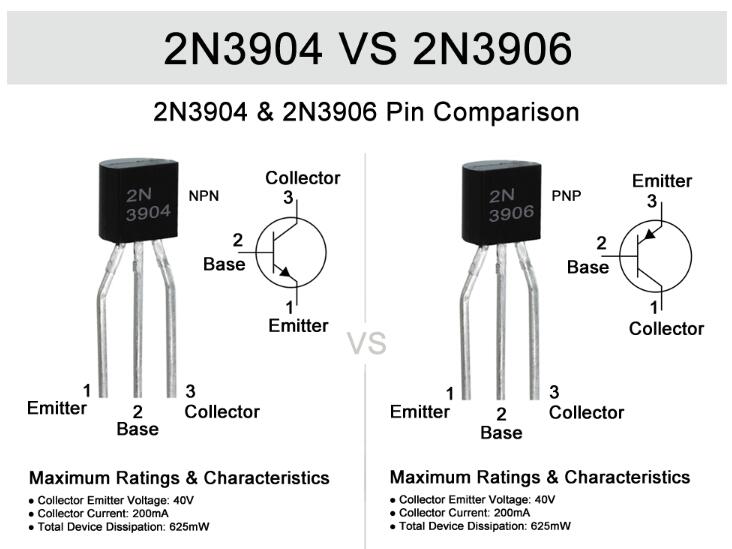
2N3904 (NPN Transistor): The 2N3904 is an NPN transistor with the following characteristics:
-
Maximum Collector Current (IC): The 2N3904 typically has a maximum collector current rating of 200 mA (milliamperes). This rating specifies the maximum current that can safely flow through the transistor's collector terminal without damaging it.
-
Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO): The 2N3904 usually has a maximum collector-emitter voltage rating of 40 volts. It signifies the maximum voltage allowed across the collector-emitter junction without risking transistor failure.
-
Current Gain (hFE or β): The current gain of the 2N3904 transistor typically falls within the range of 100 to 300. The hFE value represents the amplification capability of the transistor and indicates the ratio of the collector current (IC) to the base current (IB).
2N3906 (PNP Transistor): The 2N3906 is a PNP transistor and the complementary counterpart to the 2N3904. Here are its characteristics:
-
Maximum Collector Current (IC): The 2N3906 typically has a maximum collector current rating of 200 mA, similar to the 2N3904.
-
Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO): The 2N3906 usually has a maximum collector-emitter voltage rating of 40 volts, matching the 2N3904's rating.
-
Current Gain (hFE or β): The current gain of the 2N3906 transistor also falls within the range of 100 to 300, similar to the 2N3904.
| Ratings & Characteristics | 2N3904 | 2N3906 |
|---|---|---|
| Collector-Emitter Voltage (Vceo) | 40V | - 40V |
| Collector Current (Ic) | 200mA | - 200mA |
| Total Device Dissipation (PD) | 625mW | 625mW |
| DC Current Gain (hFE) | 30 To 300 | 30 To 300 |
| Frequency (fT) | 300 MHz | 300 MHz |
Differences:
-
Transistor Type: The primary difference between the 2N3904 and 2N3906 is their transistor type. The 2N3904 is an NPN transistor, while the 2N3906 is a PNP transistor. This difference determines the flow of current and the biasing schemes required for their respective operations.
-
Polarity: Being complementary pairs, the 2N3904 and 2N3906 have opposite polarities. The 2N3904 is used for applications requiring an NPN transistor, where the current flows from the collector to the emitter. On the other hand, the 2N3906, as a PNP transistor, is used in applications where the current flows from the emitter to the collector.
Similarities:
-
Maximum Collector Current and Voltage: Both the 2N3904 and 2N3906 have the same maximum collector current rating of 200 mA and the same maximum collector-emitter voltage rating of 40 volts. These similarities make them suitable for similar low-power applications.
-
Current Gain: The current gain for both transistors falls within the same range of 100 to 300, enabling similar amplification capabilities.
While the 2N3904 and 2N3906 have different transistor types, their similar maximum current, voltage ratings, and current gain ranges make them suitable for complementary usage when designing amplification circuits, switching applications, or constructing inverter circuits.
Always consult the datasheets provided by the manufacturer to ensure compatibility, and consider the specific requirements of your circuit when selecting the appropriate transistor.



